Resources
Get Matched to the Right Builder
FIND THE PERFECT CUSTOM HOME BUILDER WITH OUR FREE ASSESSMENT
Tired of feeling overwhelmed? Look no further. We'll match you to the right builder in the Houston area and save you months of valuable time and money you'd spend trying to find one on your own. Click below to get started!

Download The Ultimate Custom Home Building Guide
A Step-by-step guide to building your custom dream home.
Download The Ultimate Custom Home Building Checklist
Finance

Finding Lot

Best Builder

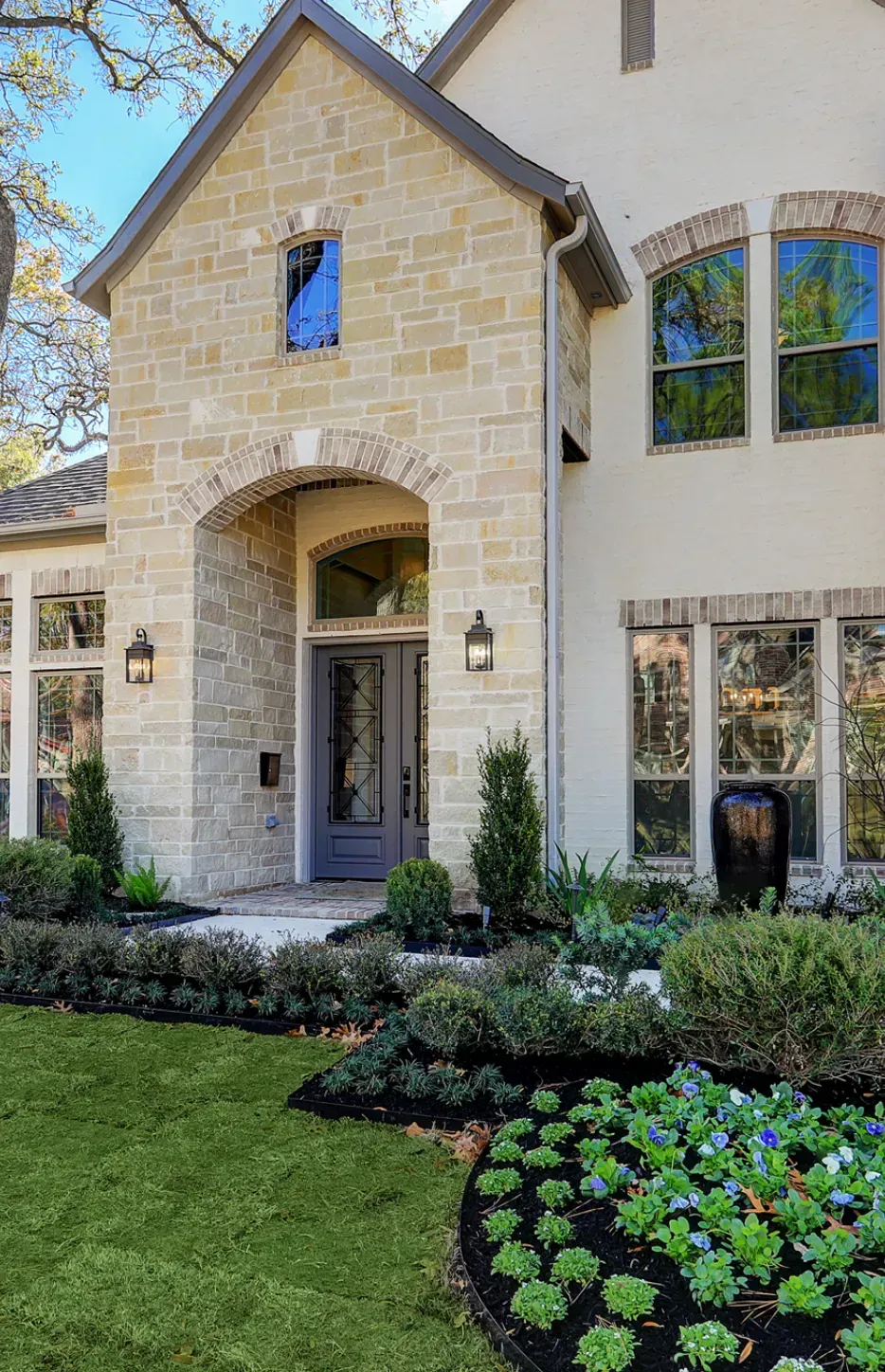
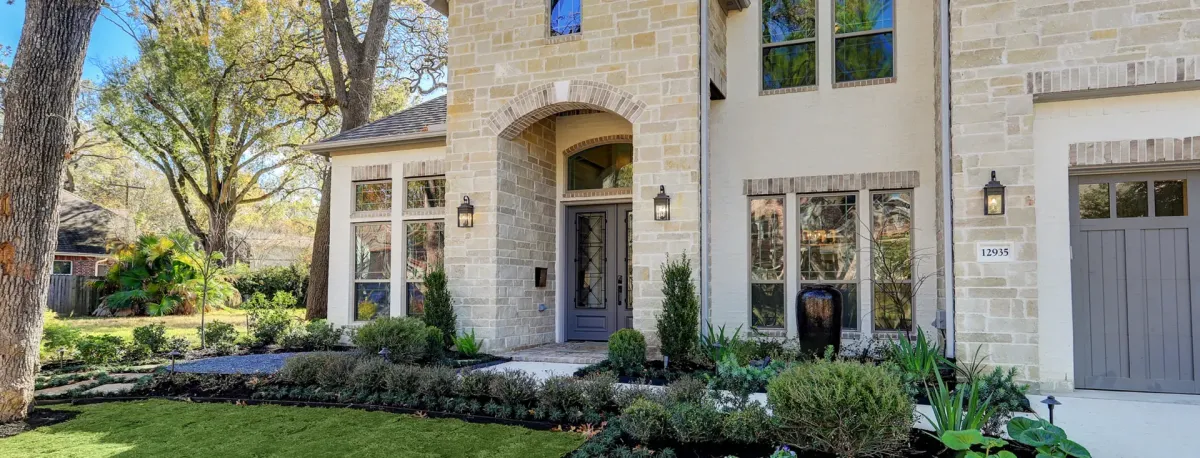
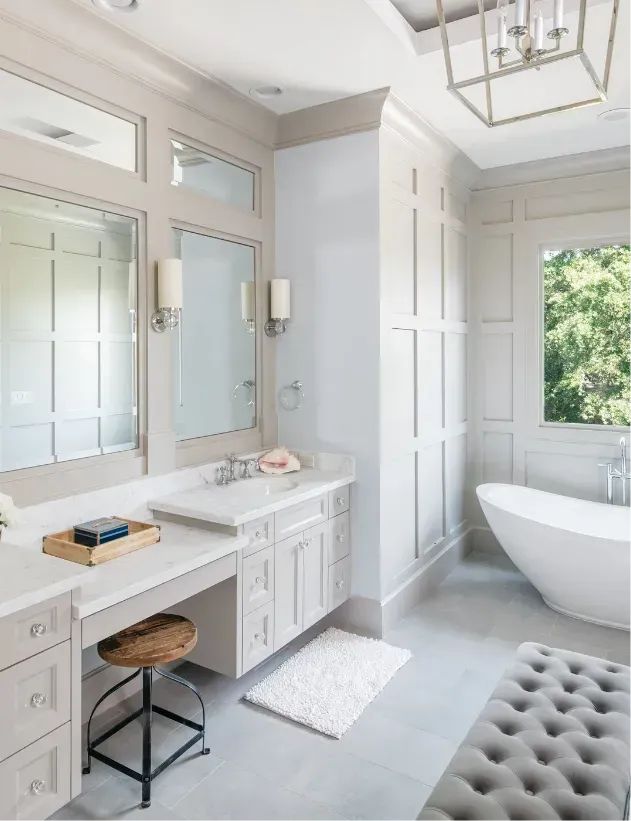
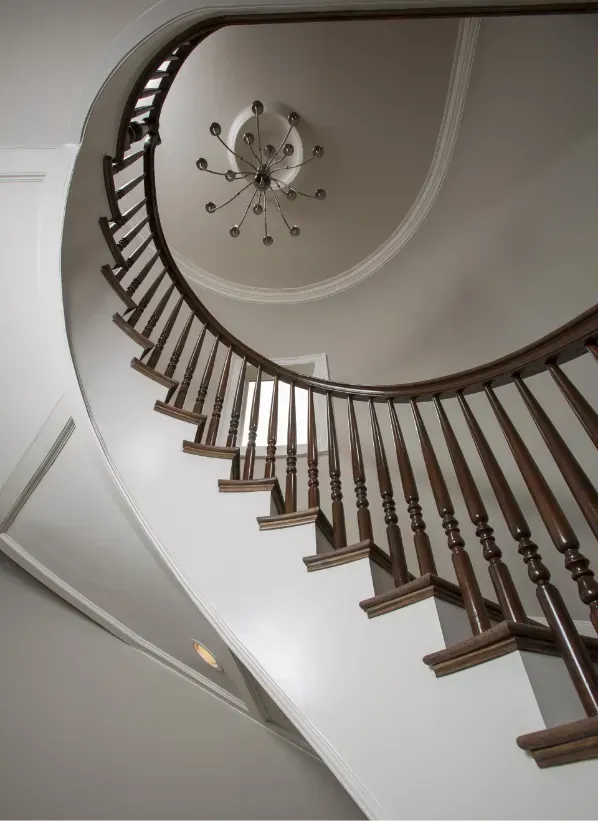
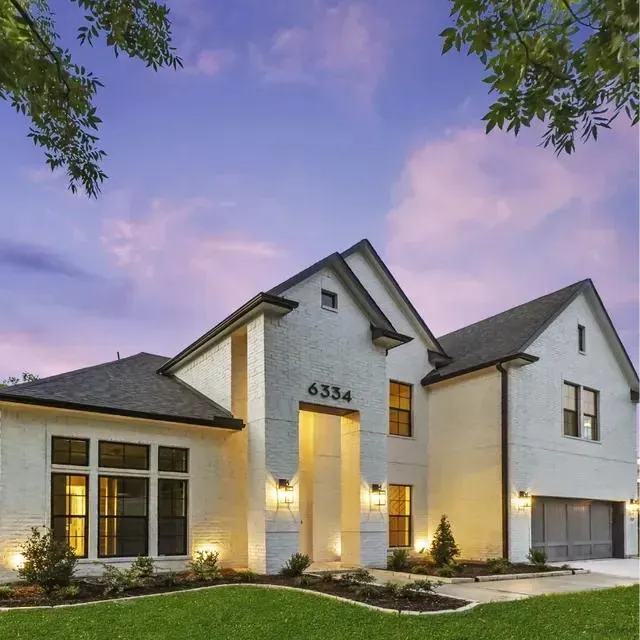
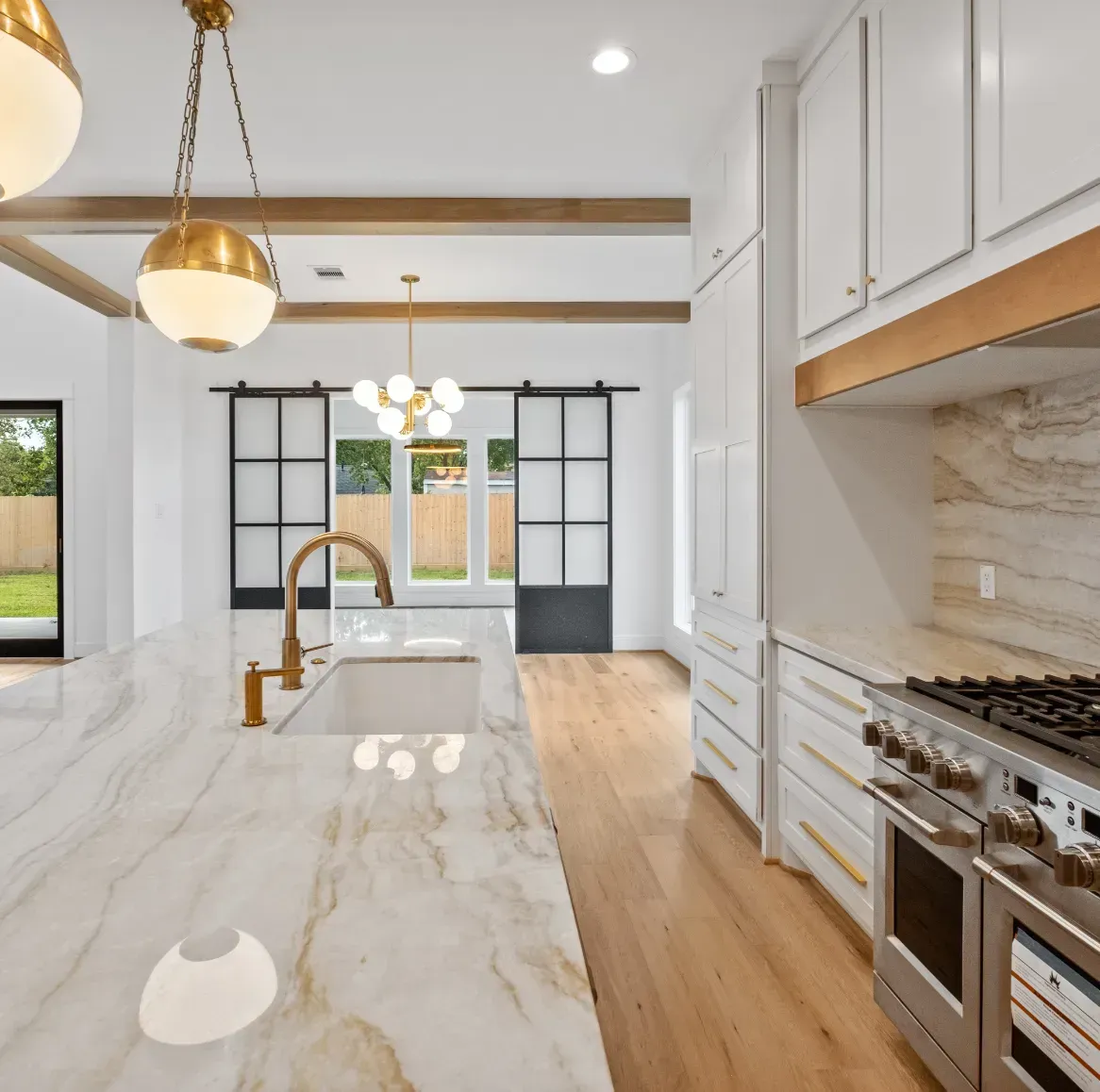
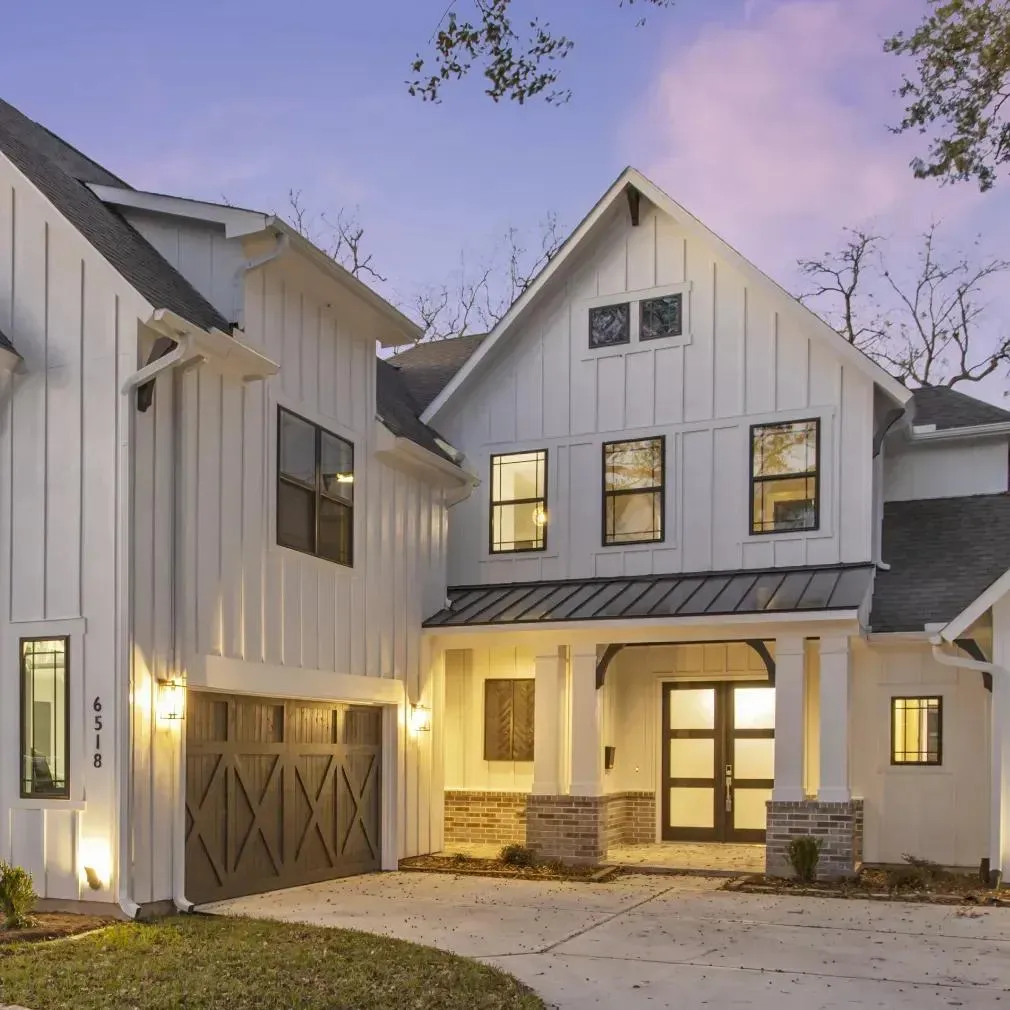
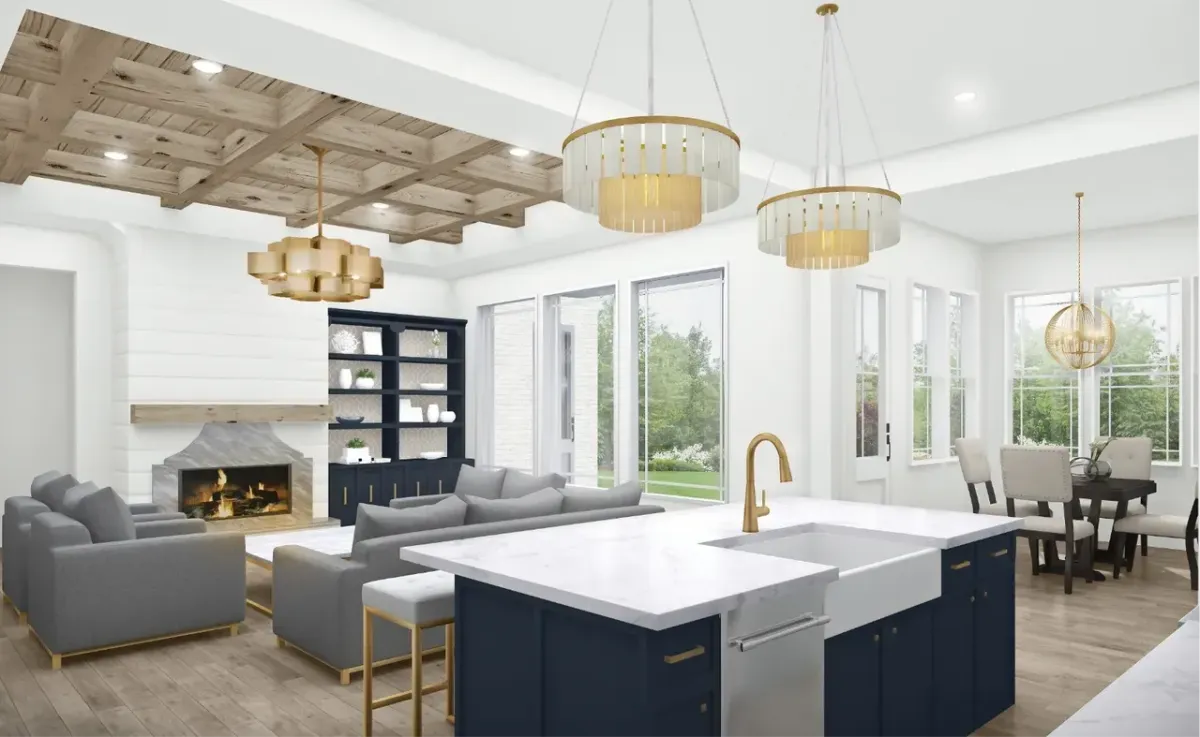
Explore Our Gallery of Custom Homes
Browse our finished projects that display the craftsmanship of the builders we’ve matched with homeowners – turning dreams into reality.
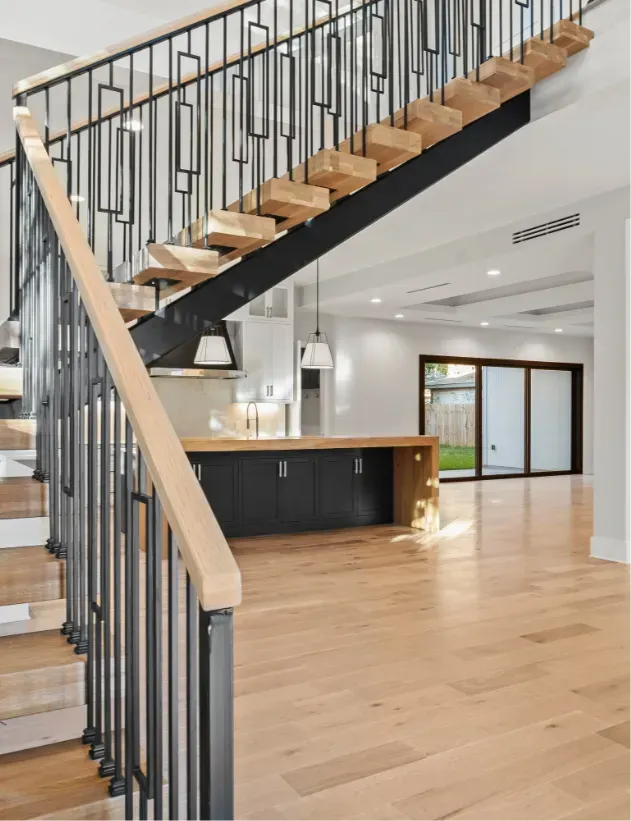









BLOG

Simplifying Zoning Laws for Your New Home Experience
Building or renovating a home can be complex due to zoning laws that affect every aspect of a project. Understanding these regulations, obtaining permits, and ensuring compliance is essential. This article provides clear guidance on zoning laws, building permits, setbacks, accessory dwelling units (ADUs), compliance, and local resources—helping homeowners in Houston, TX, and beyond navigate zoning challenges with confidence.
Key Takeaways
Zoning laws determine property use and are vital for residential projects.
Building permits require specific documentation, fees, and adherence to setbacks.
Local zoning departments and experts, such as HomeBuild Solutions, offer valuable support.
Knowing ADU regulations and zoning compliance helps avoid legal and costly issues.
Always consult zoning maps and legal advisors to ensure full regulatory compliance.
What Are Zoning Laws and Why Do They Matter for Your New Home?

Zoning laws are municipal regulations that govern how land can be used and developed. They outline what types of structures can be built on a property, as well as specific details such as building height, lot coverage, and allowable usage (residential, commercial, mixed-use, etc.). For custom home builders, zoning laws play a pivotal role in shaping design possibilities, site placement, and even the feasibility of a project—making it essential to review local codes before breaking ground.
What Do Zoning Laws Regulate in Residential Areas?
These laws manage building density, the ratio of living space to lot area, and permissible activities. They differentiate between single-family and multi-family dwellings, restrict certain commercial activities, and limit home-based businesses. Adhering to these guidelines helps prevent legal complications and fines.
How Do Zoning Districts Affect Home Construction and Renovation?
Zoning districts regulate neighborhood characteristics through building height limits, setback distances, and floor area ratios. For example, strict setback rules may limit how close a construction can be to property lines. Renovations in historic zones may need to follow preservation guidelines, influencing the overall design.
What Are Common Zoning Restrictions and Requirements?
Typical restrictions include limits on building height, minimum lot sizes, setback rules, density restrictions, and environmental preservation. Some areas also specify architectural styles or materials. Early understanding of these requirements helps streamline approvals and reduces the need for redesign.
How Do You Find and Understand Local Zoning Regulations?

Local zoning regulations are available through municipal websites, interactive zoning maps, and local government offices. These resources offer details on permitted uses, legal restrictions, and any regulatory changes that might affect your project.
Where Can You Access Zoning Maps and Local Government Resources?
Municipal websites often host interactive maps showing designated zoning districts. City planning departments and government centers also provide printed materials and one-on-one consultations, ensuring you have the most current information.
How Do You Contact Your Local Zoning Department for Information?
Visit your city or county's official website to find contact details. An in-person visit might also provide clearer, personalized guidance—especially if conditions on your property are unique.
What Tools Help Interpret Zoning Rules for Your Property?
Online GIS mapping tools, zoning analysis software, and permit calculators simplify interpretations by converting legal jargon into clear design parameters. These tools help estimate allowed floor area ratios, setback measurements, and density margins.
How to Obtain Building Permits for Your New Home Construction or Renovation?

A building permit is the official approval required to begin construction or significant renovations. It ensures your project meets safety, structural, and zoning standards.
What Is a Building Permit and When Is It Required?
A building permit verifies that a construction project complies with local building codes and zoning regulations. It is mandatory for new construction, major remodeling, or additions that impact structural integrity and safety.
What Is the Step-by-Step Process to Apply for a Building Permit?
Typically, you must submit detailed architectural plans and documentation to your local building department, pay applicable fees, and possibly attend a pre-approval meeting. Once the plans are reviewed and requirements met, a permit is issued. Revisions may be required based on feedback from zoning officials.
What Documents and Fees Are Needed for Permit Approval?
You will need blueprints, site plans, proof of ownership, environmental assessments, and sometimes engineering reports. Fees vary by project scope and cover inspections and administrative processing. Having complete documentation speeds up the approval process.
How to Handle Permit Denials or Delays?
If plans are denied or delayed due to non-compliance, request a detailed explanation and consider hiring a consultant experienced in zoning and permit applications. Revising plans to meet standards or appealing decisions can help secure the necessary permit.
What Are Setback Requirements and How Do They Impact Your Home Design?

Setback requirements dictate the minimum distance a building must have from property boundaries. They protect privacy, ensure safety, and maintain neighborhood aesthetics.
How Are Setback Distances Measured From Property Lines?
Setbacks are measured from property boundaries as specified in deeds or surveys. They usually differ for the front, rear, and sides of a lot. Accurate surveys help determine where construction is permitted.
What Exceptions or Variances Can Modify Setback Rules?
Local authorities may grant variances when strict setbacks create hardship or if unique site conditions exist. Homeowners can apply for a waiver if compliance would prevent proper use of the property without compromising safety or neighborhood standards.
How Do Setbacks Affect Building Placement and Property Use?
Setbacks influence building size, placement, and the available space for landscaping or additional structures. Proper planning of setbacks ensures compliance and maximizes both interior and exterior living areas.
How Do Zoning Laws Affect Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs) and Other Specific Home Features?

Zoning laws significantly influence the development of accessory dwelling units (ADUs), which provide extra living space on a primary residence’s lot.
What Are ADUs and How Are They Regulated by Zoning?
ADUs are self-contained living spaces that might serve as guest suites, rental units, or housing for family members. Zoning laws specify minimum lot sizes, required setbacks, parking requirements, and occupancy limits to ensure these units align with the neighborhood.
What Height and Size Restrictions Apply to ADUs?
Many jurisdictions limit ADUs to a set square footage (commonly between 600 and 1,200 square feet) and impose height restrictions to ensure they remain in scale with the primary home and surrounding properties.
How to Apply for Zoning Variances or Appeals for ADUs?
If the proposed ADU exceeds local limits, homeowners can request a variance by submitting necessary diagrams, justification, and evidence that the impact on the community will be minimal. Consulting a zoning expert can improve your chances of approval.
How Can You Ensure Zoning Compliance and Avoid Violations?

Ongoing review and careful planning are vital to maintaining zoning compliance, thereby avoiding fines, legal disputes, or construction delays.
What Are Common Zoning Violations and Their Consequences?
Violations such as building outside designated lot lines, exceeding height or density limits, or improper land use can lead to fines, mandated alterations, or even demolition. Regular documentation and site inspections help avoid these issues.
How to Use a Zoning Compliance Checklist for Your Project?
A checklist covering setback dimensions, land use, building codes, and permit requirements can be an essential tool throughout the construction process. Regular reviews ensure all specifications are met.
What Steps Should You Take if You Receive a Zoning Violation Notice?
Immediately consult a zoning lawyer or consultant, review the notice against your plans, and work with local authorities to correct the issue—whether through redesign, a variance, or an appeal—to mitigate penalties.
Where to Find Local Zoning Resources and Expert Help for Your New Home?

Navigating zoning challenges is easier with the right resources. Local government offices, online portals, and professional zoning experts provide the guidance necessary for a successful project.
How to Locate Local Zoning Departments and Online Portals?
City or county websites typically feature zoning maps, legal texts, permit applications, and contact information. Many also offer public meetings or workshops discussing zoning and building regulations.
When Should You Consult Zoning Experts or Legal Advisors?
Consult experts early in planning, when significant changes are proposed, or if questions about local regulations arise. They can assist with evaluations, variance applications, and help represent your interests during appeals.
Final Thoughts
Navigating zoning laws is a critical component of building or renovating a home. By understanding zoning restrictions, securing the necessary building permits, planning for setbacks, and knowing ADU regulations, homeowners can prevent delays and legal issues. Leveraging local resources and expert advisory services streamlines the process and maximizes property potential. With careful planning and strict adherence to regulations, your dream home remains both achievable and sustainable.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What exactly are zoning laws? A: They are local regulations that determine property use, affecting construction, renovations, and land use in residential areas.
Q: When is a building permit required? A: For new construction, major renovations, or any project that alters a property's structural integrity to ensure safety and compliance.
Q: How can I find local zoning information? A: Municipal websites, zoning maps, and local planning departments provide accurate and up-to-date zoning details.
Q: What should I do if I receive a zoning violation notice? A: Consult a zoning expert or lawyer immediately, review your plans against the notice, and work with authorities to correct the issue or request a variance.
Q: Why are setback requirements important? A: They ensure safe distances between buildings and property lines, preserving neighborhood aesthetics, privacy, and preventing conflicts.
Contact Us Today To Learn More

Phone: +1 713-304-5330
Address: 8588 Katy Fwy #450, Houston, TX 77024, United States