Understanding Zoning Variance Impact on Home Projects
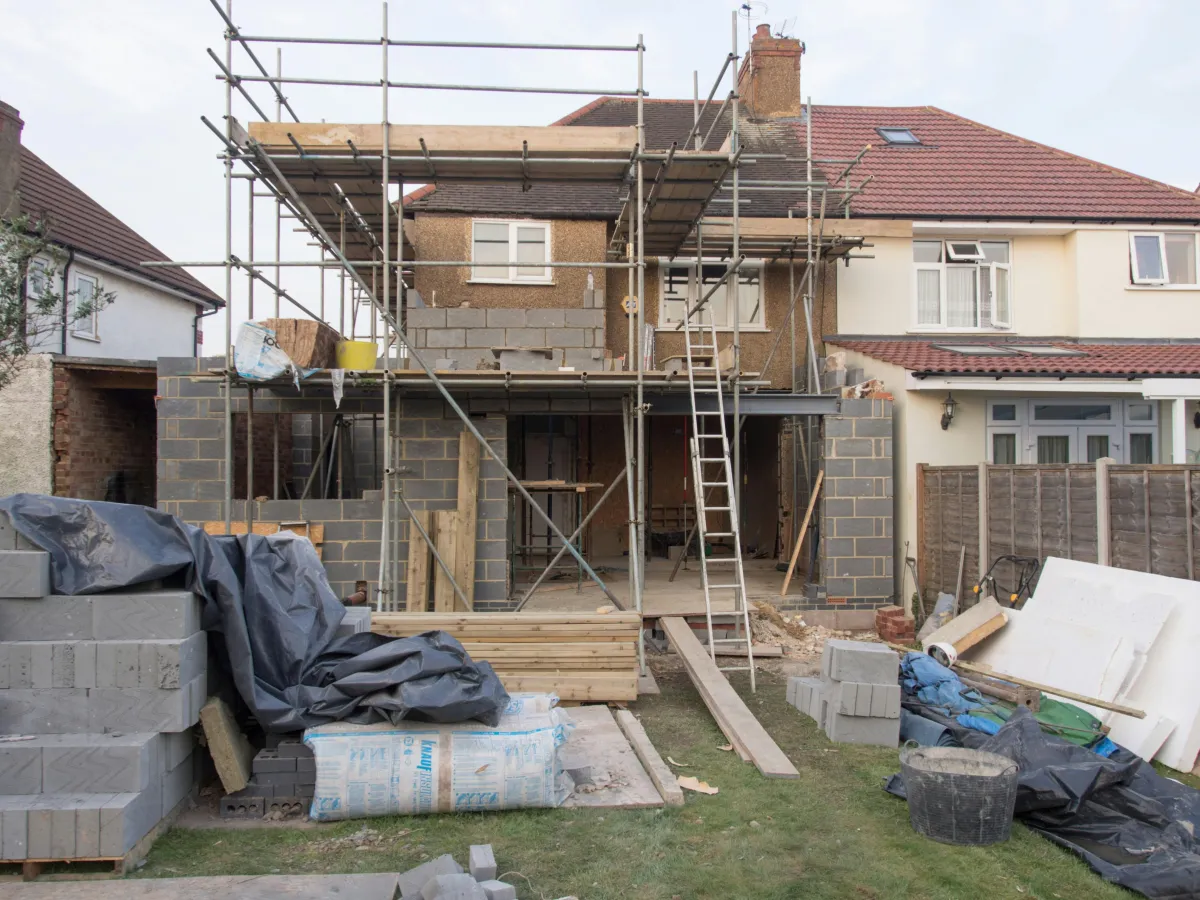
Homeowners often face unexpected hurdles when it comes to construction projects. One major issue is understanding zoning variances. This blog post explains what zoning variances are and how they impact your home projects, including applications and local government roles.
Readers will learn how to navigate the zoning variance process, addressing challenges that may arise when planning renovations, like adding a bathroom or dealing with flood insurance. This information aims to ease the confusion around zoning, helping homeowners make informed decisions while avoiding costly mistakes.
Key Takeaways
A zoning variance allows homeowners to deviate from specific zoning laws for custom projects
Understanding variances helps in navigating zoning laws and avoiding costly mistakes
Engaging with neighbors early can build support and address potential objections to the project
Compliance with zoning laws is essential to maintain property value and avoid legal issues
Submitting a well-prepared variance request increases the chances of approval from local boards
Understanding Zoning Variance Basics for Custom Home Projects

Understanding zoning variance is key for custom home projects. A zoning variance allows property owners to deviate from specific zoning laws, making it crucial in home construction. This section will identify common types of zoning variances and their applications and highlight the significance of zoning laws, especially regarding site plans and the National Flood Insurance Program.
Defining Zoning Variance and Its Role in Home Construction
A zoning variance is a formal request that allows property owners to make changes to existing zoning laws. In home construction, securing a variance may be necessary when a homeowner wants to build a renovation that does not comply with local regulations, such as setback requirements or building heights. For example, if someone plans to install a septic tank but finds the required distance from their home is too restrictive, they may apply for a variance to accommodate their needs while still adhering to federal emergency management agency guidelines and local building code regulations.
Identifying Common Types of Zoning Variances and Their Applications
Several common types of zoning variances exist that can help homeowners during their custom home projects. For instance, a use variance permits a property owner to use their land for a purpose not allowed under current zoning laws, such as converting a residential area into a home-based business. Another type is an area variance, which allows for deviations in dimensional requirements like setbacks or lot coverage, which can be crucial when plan adjustments are needed to fit a specific lot.
Use Variance: Allows different land use than currently permitted.
Area Variance: Permits changes to dimensional requirements like setbacks and height limits.
Sign Variance: Approves modifications to signage regulations for visibility.
Parking Variance: Adjusts parking space requirements for new developments.
Recognizing the Significance of Zoning Laws in Residential Design
Zoning laws play a vital role in the design and development of residential properties. They ensure that homes are built in a way that is safe and in harmony with the surrounding area. Understanding these laws can help homeowners make informed decisions and prevent costly mistakes during their custom home projects. Knowledge of zoning regulations leads to better planning and design choices, ultimately resulting in a structure that meets both personal needs and community standards:
Zoning laws ensure safety and harmony in residential areas.
Understanding these laws aids homeowners in informed decision-making.
Knowledge of zoning regulations prevents costly construction mistakes.
Good planning and design choices lead to successful custom home projects.
Evaluating the Need for a Zoning Variance in Home Projects

Assessing site-specific factors is essential to determine if a zoning variance is needed for a home project. Understanding how these variances can affect property value allows homeowners to weigh potential benefits and drawbacks. Analyzing design alternatives may also help avoid the need for a variance while still meeting regulatory requirements.
Assessing Site-Specific Factors That May Require a Variance
When assessing site-specific factors, homeowners should consider elements like the lot's size, shape, and location. For instance, an irregular lot may prevent compliance with setback requirements, prompting the need for a variance. Understanding these factors can help homeowners determine if adjustments are necessary for their custom home projects, ensuring they adhere to local zoning laws while achieving their design goals.
Understanding How Zoning Variances Affect Property Value
Understanding how zoning variances impact property value is essential for homeowners considering custom home projects. A zoning variance may allow for changes that enhance the property's appeal, such as increasing the home size or making the land use more suitable for modern needs. Homeowners should evaluate potential benefits, like increased marketability and functionality, against any drawbacks that might arise from varying local zoning laws:
Analyzing Potential Design Alternatives to Avoid a Variance
Homeowners can often avoid the need for a zoning variance by considering design alternatives early in the planning phase. For example, adjusting the layout of a home to fit within the set zoning requirements can eliminate the need for variances. This proactive approach not only simplifies the building process but also keeps the project aligned with local regulations, ensuring a smoother path toward achieving the ideal custom home.
Exploring the Zoning Variance Application Process for Homebuilders
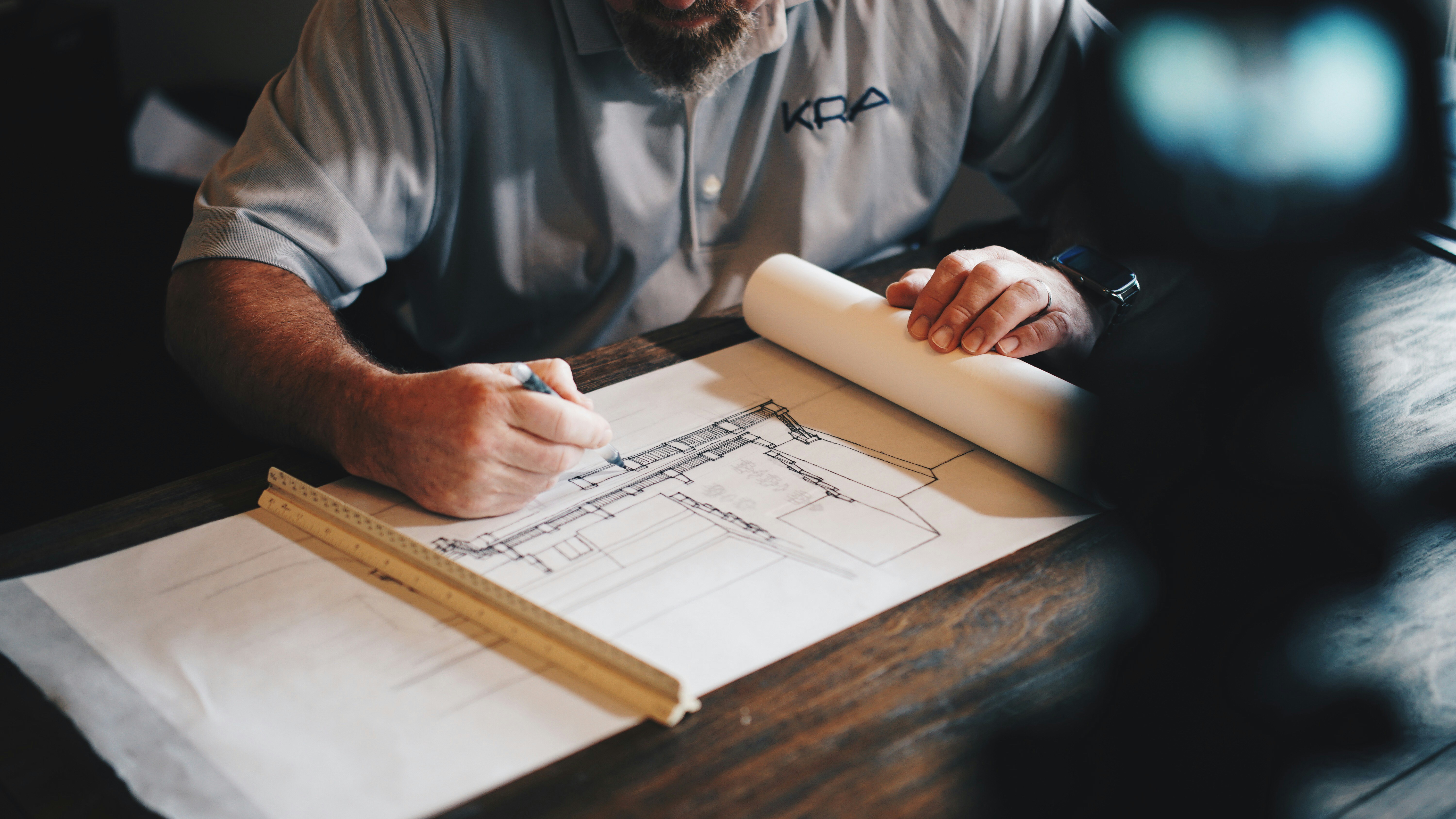

Submitting a zoning variance request involves several crucial steps that homebuilders must follow. This section will outline the process, including gathering necessary documentation and supporting materials. It will also cover preparation for the public hearing and addressing any community concerns. Understanding these elements can help ensure a smoother experience in seeking a variance for home projects.
Outlining the Steps Involved in Submitting a Variance Request
Submitting a zoning variance request involves several key steps. First, homeowners should gather essential documents, including site plans and any relevant supporting materials that clearly outline the reasons for the request. Once the application is prepared, it must be submitted to the local zoning board, followed by a public hearing where community concerns can be addressed, helping to foster understanding and support for the project.
Gathering Necessary Documentation and Supporting Materials
Gathering necessary documentation is a vital step in the zoning variance application process for homebuilders. Homeowners need to compile key materials such as site plans, photographs of the property, and written explanations of why the variance is needed. By presenting clear and comprehensive information, homeowners can effectively demonstrate their project's compliance with local regulations while addressing community concerns, ultimately increasing the chances of approval for their custom home projects.
Preparing for the Public Hearing and Addressing Community Concerns
Preparing for the public hearing is a crucial step in the zoning variance process. Homebuilders should understand community concerns that may arise regarding their proposed project. Proactive communication can help address potential issues and build support among neighbors, making it essential to present information clearly and openly.
Gather essential documents like site plans and photographs.
Prepare clear reasons for the variance request to address concerns.
Engage with the community to foster understanding and support.
Conclusion
Understanding the impact of zoning variances on home projects is essential for homeowners looking to navigate the complexities of construction. By recognizing the types of variances available and the application process, individuals can better prepare for potential challenges. Proactive planning and community engagement enhance the likelihood of approval, leading to successful custom home initiatives. Ultimately, comprehending zoning laws safeguards property value and supports informed decision-making for future developments.